Hybrid funds are a mixture of two or more asset classes.
They try to strike a balance between returns and risks.
The equity portion strives for capital appreciation to beat
inflation and the debt portion strives for stability.
Hybrid funds can be either equity-oriented funds or
debt-oriented funds.
Hybrid funds can be divided in the following manner:
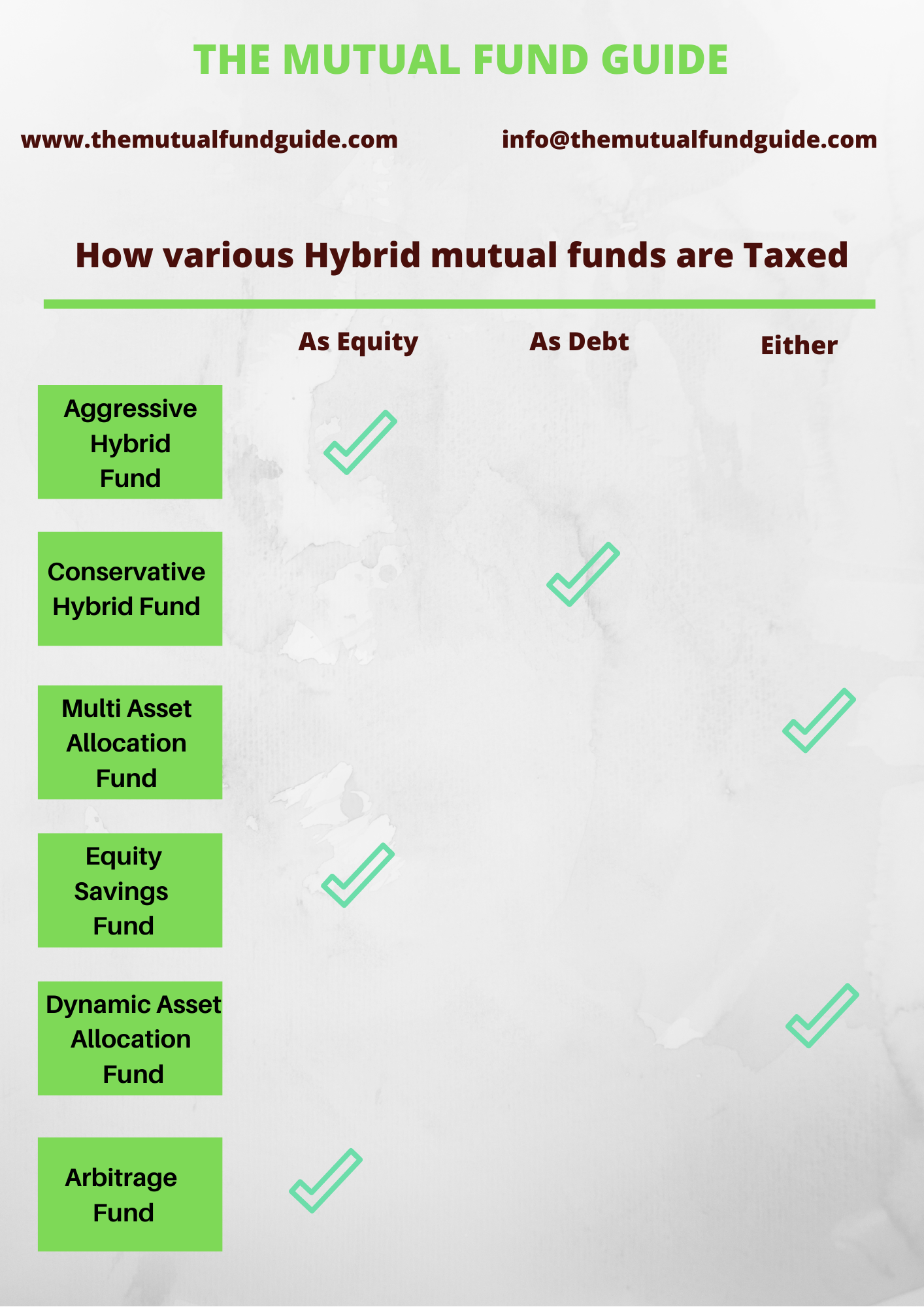
- Aggressive hybrid fund
- Conservative hybrid fund
- Multi asset allocation
- Equity savings fund
- Dynamic asset allocation fund
- Arbitrage fund
Aggressive
hybrid mutual funds
An aggressive hybrid mutual fund needs to invest a minimum
of 65% into equity at all times which can go up to 80% maximum if so desired.
The debt portion should be at a minimum of 20% at all times.
An aggressive hybrid fund has a higher equity proportion while
a conservative hybrid fund has a lower equity portion.
Therefore, an aggressive hybrid mutual fund is taxed as an
equity fund whereas a conservative hybrid fund is taxed as a debt fund.
Advantages
of Aggressive Hybrid mutual funds
An aggressive hybrid mutual fund is often perceived as a
good low risk initial step into mutual funds for a first-time mutual fund
investor.
The key word here being ‘low’.
Mutual funds were, are and will be always be risky, be it
equity or debt.
Aggressive hybrid mutual funds though tend to be less
volatile as compared to the following categories:
- Multicap mutual funds
- Large & Mid cap mutual funds
- Focused mutual funds
- Mid cap mutual funds
- Small cap mutual funds and so on.
Another key advantage of an aggressive hybrid mutual fund is
that you do not have to worry about asset allocation or re balancing.
This will be taken care by the fund manager.
If the fund manager believes the market is over valued then she
can reduce the fund’s equity allocation and if she believes the market is under
valued then she can increase the fund’s equity allocation.
This does not mean she has to, it merely means she has the
option to in case she chooses to.
What
is a conservative hybrid fund?
A conservative hybrid fund as the name suggests is a hybrid
fund but on the conservative side.
It invests predominantly in debt securities with a minimum
exposure to equities.
A conservative hybrid fund by regulation requires 75 – 90%
of its total assets invested in debt or fixed income securities.
The remaining 10 – 25% has to be allocated to equities.
Hybrid funds that invest mostly in equities are called
equity oriented funds and those that invest majorly in debt are called debt
oriented funds.
How do
conservative hybrid funds work?
A conservative hybrid fund is less volatile than an equity
fund since the major investments are in debt.
They are however not risk free.
They still have to invest a certain portion in equity which
can be volatile.
The debt portion is also prone to credit and interest rate
risk.
Advantages
of a conservative hybrid fund
A conservative hybrid fund can be considered for a short
time duration unlike equity mutual funds, that is 3 years or less.
Since a conservative hybrid fund invests mostly in debt
securities, it is stable.
This does not negate risk though, it still carries credit
and interest rate risk.
What
is a Multi Asset Fund?
A Multi Asset fund means a mutual fund that invests in three
or more asset classes.
Not all the multi asset mutual fund schemes were multi asset
funds to begin with though.
Some were merged with other schemes after SEBI’s
recategorization exercise in 2018 while some were launched after 2018 like
Motilal Oswal Multi Asset Fund and Nippon Multi Asset Fund.
This is also the only category in the mutual fund universe
where the taxation system applicable varies from scheme to scheme and there’s
no one tax system for the entire category.
How do
multi asset funds work?
Multi asset mutual funds invest a minimum of 10% each in
three or more asset classes.
10% is minimum but the fund manager can go as further as he
wants to as long as a minimum of 10% is invested in three or more asset
classes.
Assets usually invested in by Multi asset funds include but
are not limited to :
- Equity
- Debt
- International Equity
- Gold etc.
The basic idea behind a multi asset mutual fund is to try
and get the best out of each asset class with regards to both returns as well
as diversifying risks.
Different asset classes perform well at different times and
a multi asset mutual fund tries to capture each asset class when it is doing
well and reduce allocation in the asset class that is performing poorly or the
forecast for the same is poor.
Additional reading: Click Here to read our complete report on everything that you should know about a Mutual fund NAV.
Equity
Savings Fund
Equity savings fund are an open-ended hybrid fund investing
in equity, arbitrage and debt.
They need a minimum of 10% to be invested in debt funds
securities.
Equity savings fund are relatively new as a fund category,
they came into existence only after SEBI’s new regulations with regards to fund
mandate in 2018.
They invest in arbitrage opportunities to take advantage of
pricing in cash and derivatives.
Unlike other hybrid funds (except arbitrage) an equity
savings fund’s overall equity exposure is partially hedged thereby reducing its
overall volatility.
How does equity savings fund work?
Diversification
Since an equity savings fund invests in equity, debt and
arbitrage opportunities it provides decent diversification by itself.
It saves an investor the need to invest in those three
mentioned asset classes separately.
Taxation
Despite an equity savings fund investing a sizeable portion
in debt, the fund is still treated as an equity fund for tax purposes.
For tax calculation, equity funds are much more desirable
than debt equity funds.
The arbitrage position helps the fund to qualify as an
equity fund since it is the net exposure that counts eventually.
Stability
The equity portion of the fund provides capital appreciation
whereas the debt portion provides protection.
The overall structure therefore provides stability.
One still needs to do a thorough study though since debt
funds can also have credit and interest rate risk.
Dynamic
Asset allocation fund
A dynamic asset allocation fund is more popularly known as a
balanced advantage fund.
A balanced advantage fund is a type of hybrid fund.
It invests in debt, equity and arbitrage positions although
the allocation is not fixed.
It can also sit on cash if the fund manager desires so.
Unlike other hybrid funds like multi asset, aggressive and
conservative, a dynamic asset allocation or a balanced fund does not have a
fixed mandate to follow.
The fund manager can move across different asset classes
based on the prevailing market conditions.
The importance of a balanced fund is more felt during a bearish
market phase since it can cut down its equity portion and at the same time make
periodic equity purchases in the dip.
This is unlike other pure equity funds who at all times have
to maintain their mandate irrespective of the market situation.
Arbitrage
funds
Arbitrage stands for the concurrent purchase and sale of the
same asset in different markets with the intention to exploit the difference in
price.
In an arbitrage fund, a fund manager attempts to buy at a
lower price in one market and then try to sell the same asset in another market
at a higher price to make profit.
Arbitrage positions are not always and easily available
though.
For tax calculation purposes, they are treated as any other
equity fund.
What
is the difference between equity/debt and hybrid mutual funds?
A pure equity fund will be taxed as an equity fund.
A pure debt fund will be taxed as a debt fund.
There is no uniform tax rule for hybrid funds as a category
though, each fund will be taxed as per the prevailing asset allocation.
In fact, within the multi asset hybrid fund category too,
there is no uniformity with regards to taxation.
A hybrid fund is mixture of two or more asset classes,
usually equity and debt.
Whereas with an equity fund, equity is the more prominent
asset class and with a debt fund, debt.
Taxation
on hybrid funds
There is no uniform taxation rules for hybrid funds, they
are taxed based on whether the fund qualifies as an equity fund or debt fund.
LTCG
For hybrid funds that qualify as an equity fund LTCG is applied
on gains held for more
than a year and are more than 1 lakh.
The LTCG rate is 10%.
Capital gains up to 1 lakh are exempt for taxes.
There is no indexation benefit when calculating LTCG.
STCG
Short term capital gains tax better known as STCG is applied
on gains from hybrid mutual funds which are held for 12 months or less.
The STCG rate is 15%.
There is no ceiling benefit in STCG like the 1 lakh ceiling
in LTCG.
STCG is charged on from Re 1.
LTCG
For hybrid funds that qualify as a debt mutual fund, long term capital gains tax is
applied on gains held for more than 36 months.
The LTCG rate is 20% after indexation.
STCG
Short term capital gains tax is
applied on gains held for less than 36 months.
Short term capital gains are added to your income and taxed
as per your income tax slab.
For multi asset allocation funds the tax structure applied
here differs from scheme.
If a particular multi asset mutual fund has an equity
allocation of minimum 65% then it is taxed as an equity mutual fund whereas a
multi asset mutual fund that does not have a minimum 65% equity allocation is
taxed as a debt mutual fund.
For portfolio enquiries, email us with your doubts at info@themutualfundguide.com
Copyright © 2021 The Mutual Fund Guide, All rights reserved